On-Grid vs Off-Grid Solar Systems in India: Which One Should You Choose?
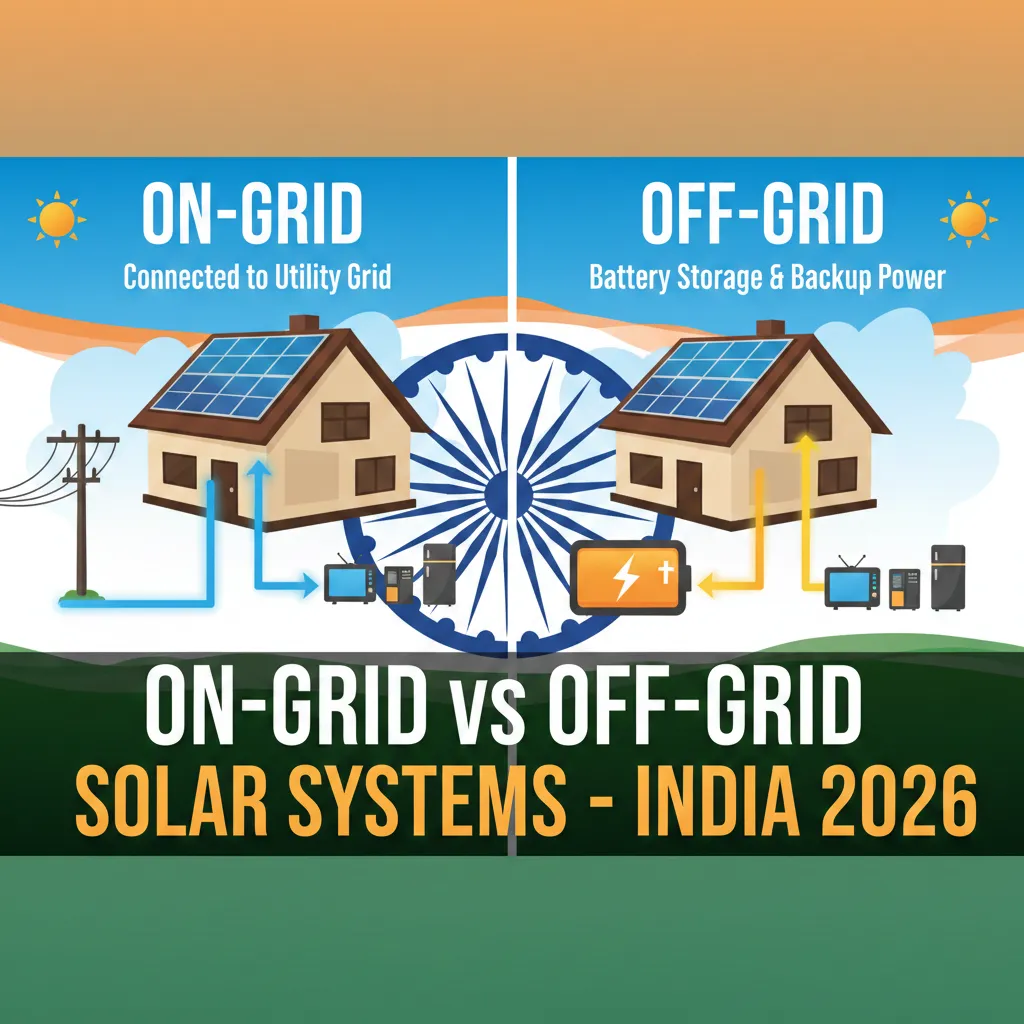
With electricity prices rising and solar technology becoming more accessible in India, homeowners are increasingly considering rooftop solar systems. But there’s an important decision to make: Should you choose an On-Grid or Off-Grid solar system?
In this 2026 guide, we’ll explain the difference between On-Grid and Off-Grid systems, their advantages, limitations, costs, and help you decide which is right for your home or business in India.
What Are On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems?
1️⃣ On-Grid Solar Systems
On-Grid (or grid-tied) systems are connected directly to the electricity grid. These systems:
- Feed excess solar electricity back to the grid through net metering
- Reduce your electricity bills
- Do not require batteries for daytime power
- Are ideal for areas with reliable grid supply
2️⃣ Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-Grid systems are independent of the electricity grid. They:
- Store electricity in batteries for nighttime use or during power outages
- Are suitable for remote areas with unreliable grid supply
- Require larger initial investment due to battery cost
- Offer complete energy independence
Key Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Systems
| Feature | On-Grid | Off-Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Connection | Yes | No |
| Batteries Required | Optional | Mandatory |
| Backup During Outages | No | Yes |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate (batteries require care) |
| Net Metering | Yes | No |
| Ideal For | Urban/Metro homes | Remote/Rural areas |
Advantages of On-Grid Solar in India
- Lower upfront cost
- Net metering benefits: Export excess power to the grid and reduce your electricity bills
- Minimal maintenance: No batteries needed for standard daytime usage
- Efficient energy use: Uses grid power when solar output is low
Considerations
- On-Grid systems cannot provide power during blackouts unless paired with battery storage.
- Requires net metering approval from the local DISCOM.
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar in India
- Complete energy independence
- Power during outages: Batteries store energy for nighttime or cloudy days
- Suitable for remote locations: Ideal for villages and farms without reliable grid access
- Scalable: Can combine with solar pumps, street lights, and small commercial setups
Considerations
- Higher upfront cost due to batteries
- Batteries need replacement every 5–10 years
- Higher maintenance and system monitoring
Which System Should You Choose in India?
Choose On-Grid if:
- You live in an urban area with reliable grid electricity
- You want to save on electricity bills using net metering
- You prefer lower installation and maintenance costs
- You do not need power backup during outages
Choose Off-Grid if:
- You live in rural or remote areas with unreliable or no grid access
- You want full energy independence
- You are ready to invest in battery storage for backup power
- You want solar for applications like water pumps or isolated buildings
Cost Comparison in India (2026)
| System Type | Approx. Cost per kW (INR) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| On-Grid | ₹50,000 – ₹70,000 | Subsidy available for residential systems up to 3 kW |
| Off-Grid | ₹80,000 – ₹1,20,000 | Higher due to battery storage |
| Battery Replacement | ₹20,000 – ₹50,000 every 5–10 years | Required for Off-Grid systems |
Government subsidies (PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana) may reduce upfront costs for residential installations.
Maintenance Tips for Both Systems
- Clean solar panels regularly to maintain efficiency
- Inspect inverters and batteries (if off-grid) annually
- Use energy-efficient appliances to reduce load on the system
- Monitor output via apps or smart meters
Final Verdict: Which Is Right for You?
- Urban/Homeowners with Grid Access: On-Grid systems are cost-effective, easy to maintain, and allow net metering benefits.
- Rural/Remote Locations: Off-Grid solar systems ensure reliable power even without grid electricity, but require higher investment.
- Hybrid Option: Combining on-grid with battery storage provides best of both worlds — net metering savings with backup power.
In 2026, India’s solar technology is mature, reliable, and financially accessible. Selecting the right system depends on your location, energy needs, and budget.



